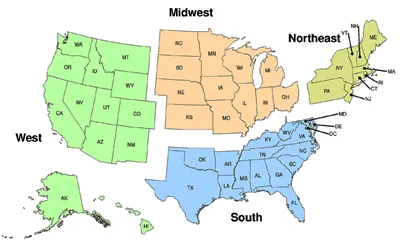
Norovirus, commonly referred to as the stomach flu, is experiencing a resurgence in various regions across the United States, raising alarms among health officials. According to recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the number of reported cases has increased dramatically, with some jurisdictions experiencing double the burden compared to previous years. ‘This is a significant rise,’ said Dr. Karen D. Johnson, an epidemiologist at the CDC. ‘Norovirus spreads rapidly, especially in crowded places such as schools and nursing homes, and we must be vigilant in our prevention efforts.’ The CDC has noted that states such as New York, California, and Texas are currently seeing the highest spikes in infections. Health experts urge people to maintain rigorous hygiene practices, including frequent handwashing, to help curb the spread of the virus. Symptoms of norovirus typically include vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain, and nausea, often leading to dehydration, particularly in vulnerable populations such as the elderly and young children. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary. The increase in cases is reportedly linked to various outbreaks traced back to contaminated food sources and close contact in communal settings. As we enter the peak winter season, health authorities are on high alert and are advocating for increased awareness around this highly contagious virus. ‘Public education is key,’ emphasized Dr. Johnson. ‘Understanding how norovirus spreads can empower individuals to take proactive steps to safeguard their health and the health of those around them.’
Norovirus Cases Surge Across the U.S.: Health Officials Warn of Risks